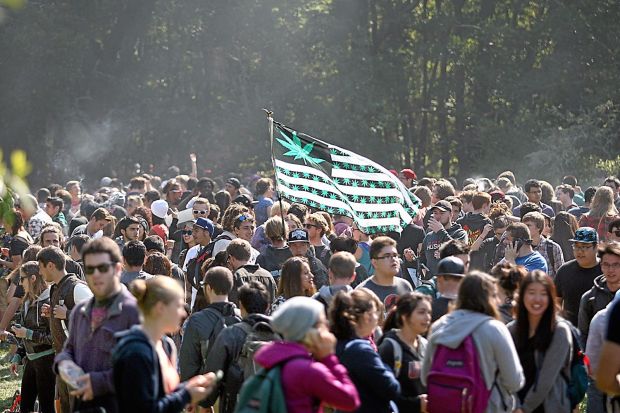
This past saturday, the “unofficial holiday” known as 4/20 occurred, landing on the first day of Passover and the day before Easter Sunday. Events celebrating the “holiday” appeared throughout the US and Canada, with some events even occurring in the UK and New Zealand.
Those in non-cannabis culture countries who see jokes and mentions of the event may be asking “why is this a holiday?” or even “what does 420 even have to do with weed?”. Well, in order to understand the first question, we need to first look at the second.
The association of 420 and marijuana started in the 1970’s in San Rafael, California. A group of high school students and marijuana enthusiasts, going by the name of “Waldos”, met up at 4:20 pm every afternoon by a statue in order to search for that they believed to be a was a pot plot. They never did find the pot plot, but began using the term “420” as a code for anything pot-related.
How did the term expand beyond just the group of Waldos? One of them became involved with the band Grateful Dead, when they worked with said Waldos father on a real estate deal. The bassist of the Grateful Dead became friends with the Waldo, and heard the 420 slang and took a liking to it, kick-starting its spread throughout the United States.
The “holiday” itself came around starting in 1990, and has grown in subsequent years. The event really bloomed internationally in cannabis culture countries in the early 2010’s, when 420 became a popular meme after the legalization of recreational marijuana in the state of Colorado. Recreational marijuana use already existed in Canada, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium, Portugal, and Chile, although celebration of the 420 event only existed, and only really continues to exist in Canada.
Marijuana remains almost entirely illegal throughout most of the rest of the world, which keeps celebration of the event mostly in North America. Cultural differences and perceptions of marijuana also locks the event within North America for the most part, although the internet has been spreading awareness of the event throughout the West.